


Next: Implementation Issues
Up: Communication Library Primitives
Previous: Communication Primitive: COMBINE
Given an 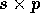 matrix distributed across a p processor
partition, where q = s p, the GATHER Primitive converts the
data layout such that the entire s p elements are held in a
matrix distributed across a p processor
partition, where q = s p, the GATHER Primitive converts the
data layout such that the entire s p elements are held in a 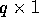 array local to a single processor. A simple algorithm
consists of logically replicating the input data such that there are
p copies in contiguous memory, and then calling the TRANSPOSE
Communication Primitive. Note that the inverse operation to this
primitive is that of SCATTER, where a single column of q
elements of data on one processor is divided into p equal-sized
chunks and transposed to fill a
array local to a single processor. A simple algorithm
consists of logically replicating the input data such that there are
p copies in contiguous memory, and then calling the TRANSPOSE
Communication Primitive. Note that the inverse operation to this
primitive is that of SCATTER, where a single column of q
elements of data on one processor is divided into p equal-sized
chunks and transposed to fill a  distributed
layout. The analysis for these two primitives is given in
Eq. (3).
distributed
layout. The analysis for these two primitives is given in
Eq. (3).



Next: Implementation Issues
Up: Communication Library Primitives
Previous: Communication Primitive: COMBINE
David A. Bader
dbader@umiacs.umd.edu
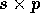 matrix distributed across a p processor
partition, where q = s p, the GATHER Primitive converts the
data layout such that the entire s p elements are held in a
matrix distributed across a p processor
partition, where q = s p, the GATHER Primitive converts the
data layout such that the entire s p elements are held in a 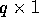 array local to a single processor. A simple algorithm
consists of logically replicating the input data such that there are
p copies in contiguous memory, and then calling the TRANSPOSE
Communication Primitive. Note that the inverse operation to this
primitive is that of SCATTER, where a single column of q
elements of data on one processor is divided into p equal-sized
chunks and transposed to fill a
array local to a single processor. A simple algorithm
consists of logically replicating the input data such that there are
p copies in contiguous memory, and then calling the TRANSPOSE
Communication Primitive. Note that the inverse operation to this
primitive is that of SCATTER, where a single column of q
elements of data on one processor is divided into p equal-sized
chunks and transposed to fill a  distributed
layout. The analysis for these two primitives is given in
Eq. (3).
distributed
layout. The analysis for these two primitives is given in
Eq. (3).