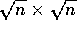 element parallel variable data array.
element parallel variable data array.
A typical operation in our image processing algorithms requires that
each pixel be updated based on the pixel values of a small
neighborhood. Such an operation amounts to a regular grid shift of a
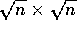 element parallel variable data array.
element parallel variable data array.
Two phases occur in the regular grid shift:
 = Each node accesses its own local memory to shift up its own subgrid;
= Each node accesses its own local memory to shift up its own subgrid;
 = Each node sends and receives the elements lying along
the shifted subgrid border.
= Each node sends and receives the elements lying along
the shifted subgrid border.
For 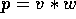 processors,
processors,  takes O
takes O =
O
=
O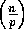 time.
time.
Next we make some observations about the communication phase:
 sends to
sends to  ,
,  receives from
receives from  ;
;
This communication pattern is a block permutation, and the time
complexity for this operation is given in (3). Note
that each node must send a constant number of upper rows of its
subgrid to its north adjacent node in the major grid. There are
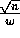 elements along this border. Thus,
elements along this border. Thus,  , and the communications time is as follows:
, and the communications time is as follows:

Therefore, a regular grid shift of a 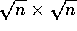 data
array on p nodes connected by a CM-5 fat-tree has the following time
and communication complexity:
data
array on p nodes connected by a CM-5 fat-tree has the following time
and communication complexity: